As practice haploid v. diploid answer key takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world of cellular diversity, where the fundamental differences between haploid and diploid cells shape the very essence of life. This exploration promises to illuminate the significance of haploidy and diploidy, unraveling their evolutionary history and implications for different organisms.
Delving into the intricacies of haploid and diploid life cycles, we will uncover the mechanisms by which these cells reproduce, contrasting their advantages and disadvantages. Through a comparative analysis, we will identify the key distinctions that set these two cellular states apart, providing a comprehensive understanding of their roles in the grand tapestry of life.
Haploid and Diploid Basics: Practice Haploid V. Diploid Answer Key

Haploid cells contain half the number of chromosomes as diploid cells. They are typically produced by meiosis, a specialized cell division that occurs during the formation of gametes (sex cells). Diploid cells, on the other hand, contain two complete sets of chromosomes and are formed by the fusion of two haploid gametes during fertilization.
Significance of Haploidy and Diploidy, Practice haploid v. diploid answer key
- Haploidy:Haploid cells are important for sexual reproduction as they allow for the mixing of genetic material from two parents, leading to genetic diversity.
- Diploidy:Diploid cells are essential for the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms, as they provide genetic stability and allow for the regulation of gene expression.
Haploid Life Cycles

Haploid organisms spend the majority of their life cycle in the haploid phase, with the diploid phase only occurring briefly during fertilization. This life cycle is common in fungi, algae, and some protists.
Reproduction in Haploid Organisms
Haploid organisms reproduce through sexual reproduction. During fertilization, two haploid gametes fuse to form a diploid zygote. The zygote then undergoes meiosis to produce haploid spores, which grow into new haploid individuals.
Examples of Organisms with Haploid Life Cycles
- Fungi (e.g., yeast, mold)
- Algae (e.g., Chlamydomonas)
- Some protists (e.g., Paramecium)
Diploid Life Cycles
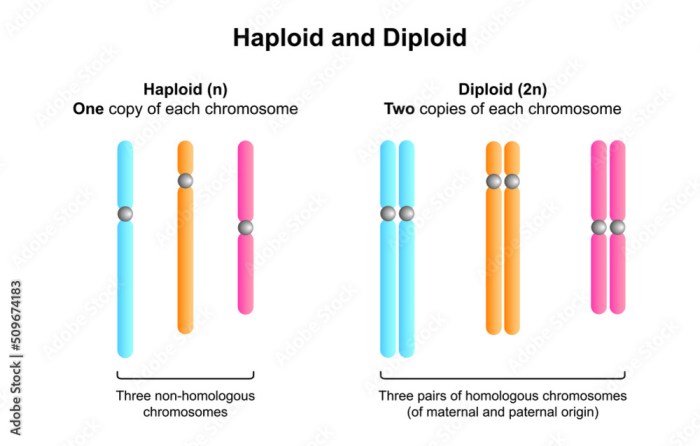
Diploid organisms spend the majority of their life cycle in the diploid phase, with the haploid phase only occurring during gamete formation. This life cycle is found in plants, animals, and most other multicellular eukaryotes.
Reproduction in Diploid Organisms
Diploid organisms reproduce through both sexual and asexual reproduction. In sexual reproduction, two haploid gametes fuse to form a diploid zygote. The zygote then develops into a diploid individual. In asexual reproduction, a diploid individual produces offspring that are genetically identical to itself.
Examples of Organisms with Diploid Life Cycles
- Plants (e.g., trees, flowers)
- Animals (e.g., humans, insects)
- Most other multicellular eukaryotes
Comparison of Haploid and Diploid Life Cycles
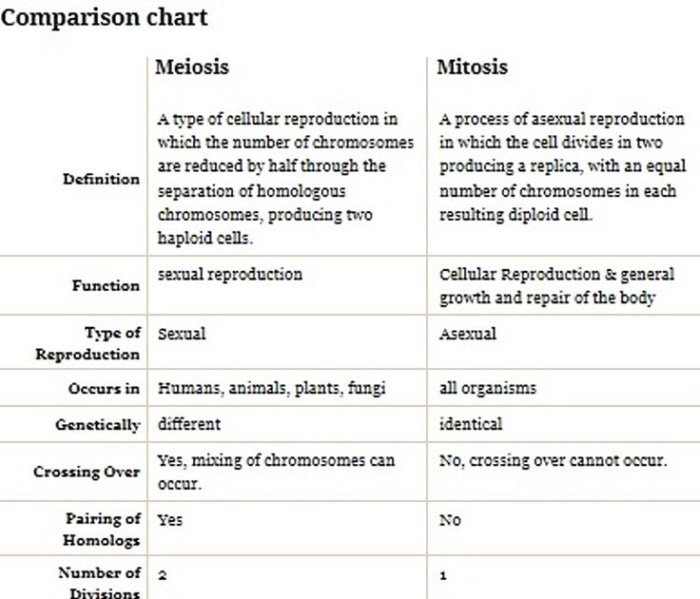
| Characteristic | Haploid Life Cycle | Diploid Life Cycle |
|---|---|---|
| Dominant Phase | Haploid | Diploid |
| Reproduction | Sexual | Sexual and asexual |
| Genetic Diversity | High | Low |
| Examples | Fungi, algae, some protists | Plants, animals, most multicellular eukaryotes |
Evolution of Haploid and Diploid Life Cycles
The evolution of haploid and diploid life cycles is a complex and ongoing process. Haploid life cycles are thought to have evolved first, with diploid life cycles evolving later as a way to increase genetic stability and complexity.
The future of haploid and diploid life cycles is uncertain. It is possible that haploid life cycles will become more common in certain environments, while diploid life cycles may become more common in others. It is also possible that new types of life cycles will evolve, combining elements of both haploid and diploid cycles.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the primary distinction between haploid and diploid cells?
Haploid cells possess a single set of chromosomes, while diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes.
How do haploid organisms reproduce?
Haploid organisms typically reproduce through asexual reproduction, such as mitosis or budding, which results in offspring genetically identical to the parent.
What are the advantages of a diploid life cycle?
Diploid life cycles provide genetic diversity through the process of meiosis, which shuffles and recombines chromosomes, resulting in offspring with unique genetic combinations.