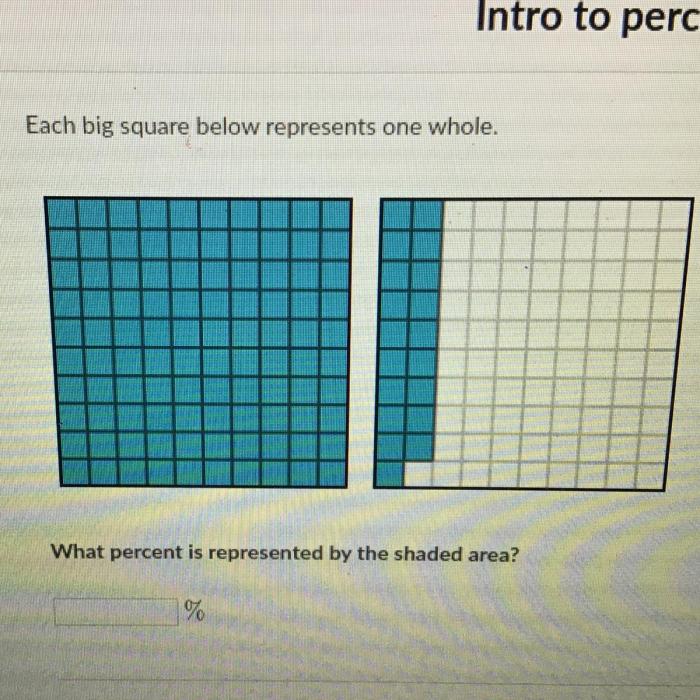
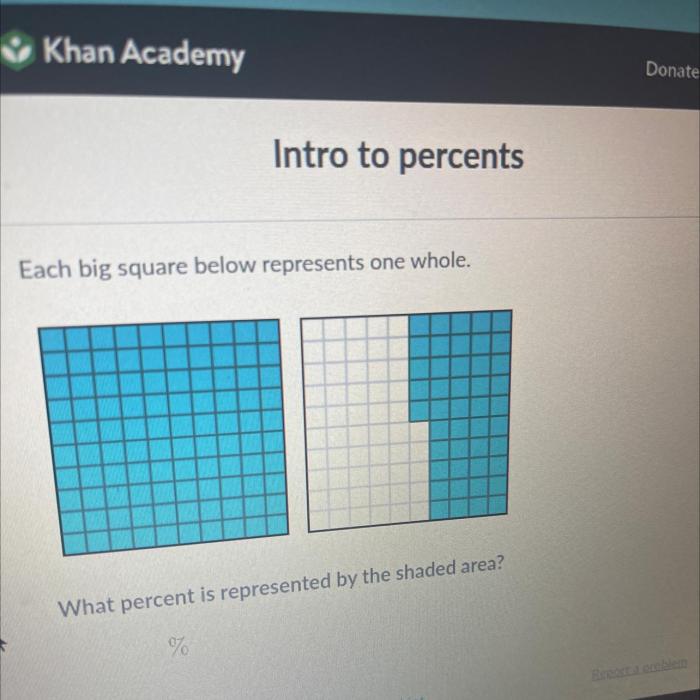
Each big square below represents one whole. – Each big square below represents one whole, an essential concept that permeates mathematical thinking and everyday life. This representation serves as a cornerstone for understanding numerical equivalence, visual representation, and various applications across disciplines. Its simplicity and versatility make it a powerful tool for enhancing mathematical understanding and problem-solving.
The numerical equivalence between the big square and the whole provides a solid foundation for mathematical operations. It allows for the representation of fractions, decimals, and percentages as parts of a whole. This equivalence facilitates comparisons, calculations, and the development of number sense.
Definition and Representation: Each Big Square Below Represents One Whole.
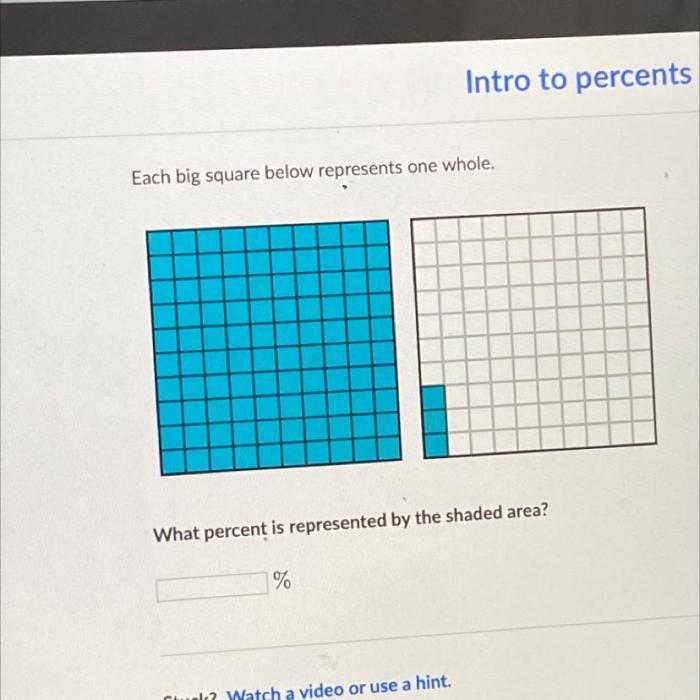
The concept of “each big square below represents one whole” is a visual representation of a whole as a large square divided into smaller squares. Each small square represents a fraction of the whole, and the sum of all the small squares equals the whole.
For example, a square divided into 4 equal smaller squares would represent the whole, and each small square would represent 1/4 of the whole.
Numerical Equivalence
The big square and the whole have a numerical equivalence. The area of the big square represents the total value of the whole, and the area of each small square represents the value of the fraction it represents.
For example, if the big square has an area of 100 square units, and each small square has an area of 25 square units, then each small square represents 1/4 of the whole (25/100 = 1/4).
Visual Representation
The visual representation of the big square and the smaller squares conveys the concept of a whole by breaking it down into smaller, more manageable parts.
This visual representation can be used to illustrate fractions, ratios, and proportions. For example, a square divided into 10 equal smaller squares can be used to represent the fraction 3/10, where 3 of the small squares are shaded.
Applications in Mathematics
The representation of a whole as a big square with smaller squares has numerous applications in mathematics:
- Simplifying fractions: By breaking down a fraction into smaller parts, it becomes easier to simplify it.
- Solving proportions: The visual representation helps students understand the concept of proportions and solve problems involving ratios.
- Understanding percentages: By dividing the big square into 100 smaller squares, it becomes easier to visualize and understand percentages.
Use in Real-Life Scenarios
The representation of a whole as a big square with smaller squares is not limited to mathematics. It has practical applications in various fields:
- Architecture: Architects use this representation to design buildings and structures, dividing the whole space into smaller sections.
- Engineering: Engineers use this representation to design machines and systems, breaking down complex systems into smaller components.
- Business: Businesses use this representation to divide tasks and projects into smaller, more manageable parts.
Educational Implications
The representation of a whole as a big square with smaller squares has significant educational implications:
- Enhancing mathematical understanding: This representation helps students visualize and understand mathematical concepts more concretely.
- Facilitating problem-solving: By breaking down problems into smaller parts, students can develop problem-solving strategies.
- Improving mathematical communication: This representation provides a common language for students to communicate mathematical ideas.
Comparison with Other Representations
The representation of a whole as a big square with smaller squares is not the only way to represent a whole. Other representations include:
- Circle divided into sectors
- Line segment divided into equal parts
- Set of objects
Each representation has its advantages and disadvantages. The big square with smaller squares representation is particularly useful for visualizing fractions and proportions.
Extensions and Generalizations, Each big square below represents one whole.
The representation of a whole as a big square with smaller squares can be extended and generalized to more complex mathematical concepts:
- Representing decimals: By dividing the big square into 1000 smaller squares, it becomes possible to represent decimals.
- Representing rational numbers: By using different sizes of smaller squares, it becomes possible to represent rational numbers.
- Representing irrational numbers: By using an infinite number of smaller squares, it becomes possible to represent irrational numbers.
Questions and Answers
What is the purpose of representing each big square as one whole?
This representation provides a concrete and intuitive understanding of fractions, decimals, and percentages as parts of a whole.
How does this representation aid in problem-solving?
By visualizing the relationship between parts and the whole, it simplifies complex mathematical operations and enhances problem-solving strategies.
What are some practical applications of this concept outside of mathematics?
This representation finds applications in fields such as engineering, architecture, design, and everyday measurement tasks.