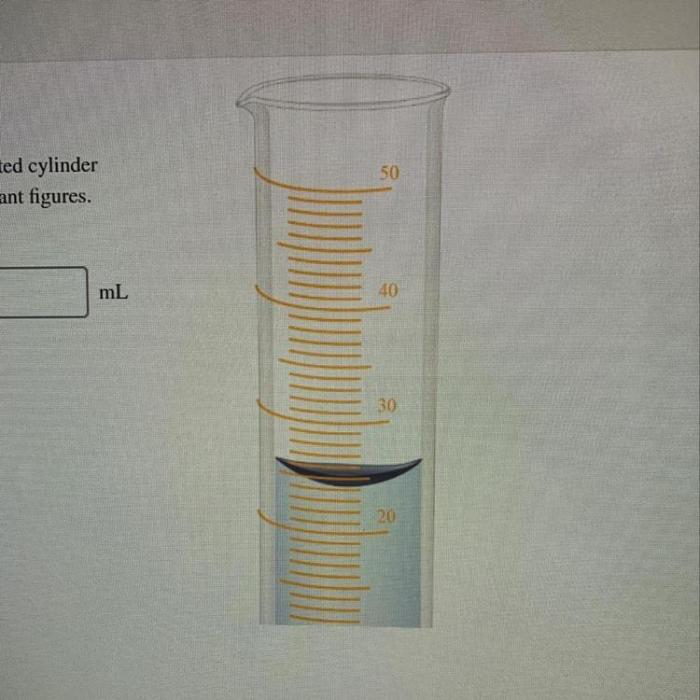
The given graduated cylinder is calibrated in milliliters ml – The graduated cylinder, an indispensable tool in various scientific and laboratory settings, plays a crucial role in precise volume measurements. This guide delves into the intricacies of graduated cylinders calibrated in milliliters (mL), exploring their calibration, units of measurement, reading techniques, and applications.
Embark on a journey of scientific exploration, where precision and accuracy reign supreme.
Understanding the principles behind graduated cylinders and their calibration ensures reliable and reproducible measurements. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the topic, empowering readers with the knowledge and skills to confidently navigate the world of volume measurement.
1. Graduated Cylinder Basics
A graduated cylinder is a cylindrical container used to measure the volume of liquids. It has a narrow, calibrated neck with graduations marked in milliliters (mL) or other units of volume. Graduated cylinders are used in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine, for precise volume measurements.
There are different types of graduated cylinders available, including:
- Class A graduated cylinders: These are high-quality cylinders with narrow necks and precise graduations. They are typically used for accurate measurements in laboratory settings.
- Class B graduated cylinders: These are less precise than Class A cylinders but are suitable for general-purpose measurements.
- Disposable graduated cylinders: These are made of plastic and are intended for single-use applications.
When using a graduated cylinder, it is important to ensure accuracy and precision. This involves:
- Selecting the appropriate size and type of graduated cylinder for the measurement.
- Positioning the cylinder vertically and at eye level.
- Reading the volume at the bottom of the meniscus (the curved surface of the liquid).
2. Calibration of Graduated Cylinders

Calibration refers to the process of verifying and adjusting the accuracy of a graduated cylinder. This involves comparing the volume indicated by the cylinder with a known standard volume. Calibration is typically performed by a certified laboratory or using a calibration solution.
The importance of proper calibration cannot be overstated. An uncalibrated or incorrectly calibrated graduated cylinder can lead to inaccurate measurements and compromised experimental results.
3. Units of Measurement
The metric system is widely used for measuring volume, and the milliliter (mL) is a common unit of volume. One milliliter is equal to one cubic centimeter (cm 3). Other units of volume include the liter (L), which is equal to 1000 mL, and the microliter (µL), which is equal to 0.001 mL.
It is important to understand the conversion between milliliters and other units of volume to ensure accurate measurements.
4. Reading Graduated Cylinders
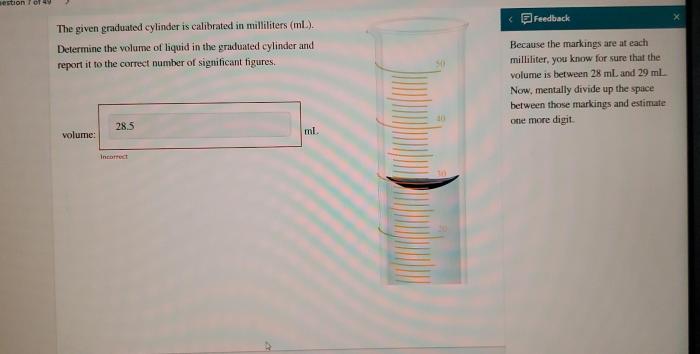
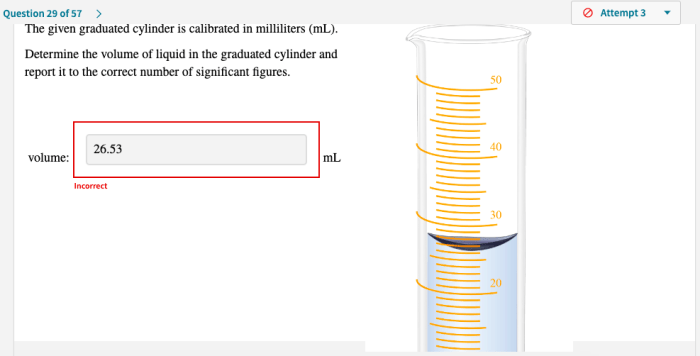
Reading the graduations on a graduated cylinder requires careful observation. The graduations are typically marked in milliliters or other units of volume. To read the volume, you should:
- Position the graduated cylinder vertically and at eye level.
- Read the volume at the bottom of the meniscus.
- Estimate the volume between graduations, if necessary.
Estimating volume between graduations requires interpolation, which can introduce some error. To minimize error, it is important to use a graduated cylinder with fine graduations and to read the volume carefully.
5. Applications of Graduated Cylinders
Graduated cylinders are widely used in various fields, including:
- Chemistry: Measuring volumes of liquids for experiments, titrations, and preparing solutions.
- Biology: Measuring volumes of liquids for cell cultures, media preparation, and enzyme assays.
- Medicine: Measuring volumes of liquids for drug preparation, blood sampling, and urinalysis.
- Education: Demonstrating volume measurements and teaching basic laboratory techniques.
While graduated cylinders are versatile tools, they have certain limitations. For very small volumes, micropipettes or burettes are more appropriate. For large volumes, volumetric flasks or graduated beakers may be used.
Expert Answers: The Given Graduated Cylinder Is Calibrated In Milliliters Ml
What is the purpose of calibrating a graduated cylinder?
Calibration ensures that the graduations on the cylinder accurately represent the volume of liquid they contain, minimizing measurement errors.
How do I read the graduations on a graduated cylinder?
Align the bottom of the meniscus (the curved surface of the liquid) with the graduation line to obtain the volume reading.
What are the sources of error when using a graduated cylinder?
Errors can arise from parallax, improper calibration, or reading the meniscus incorrectly.
