Boyle’s and charles law gizmo answers – Welcome to the realm of gas laws, where Boyle’s and Charles’ Law Gizmo Answers unveil the fascinating world of gas behavior. Embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of pressure, volume, and temperature, discovering their intricate relationships that shape the gaseous realm.
Prepare to delve into a comprehensive exploration of Boyle’s Law, unraveling the inverse relationship between pressure and volume, and Charles’ Law, revealing the direct relationship between temperature and volume. These fundamental principles form the cornerstone of gas law understanding, providing a gateway to comprehending the behavior of gases in diverse applications.
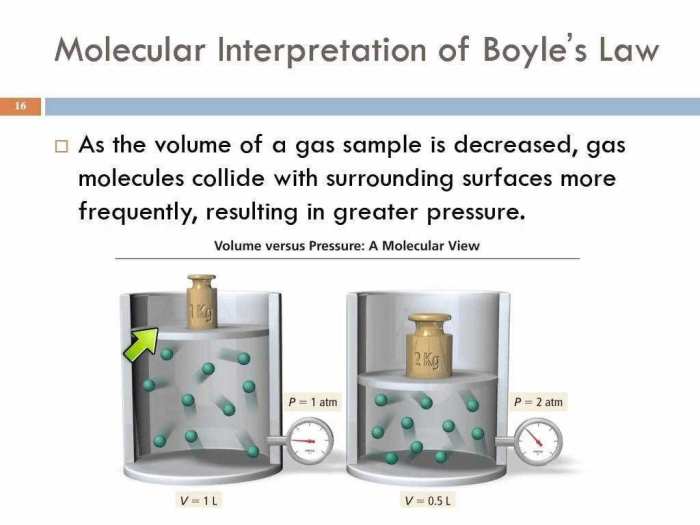
Boyle’s Law
Boyle’s Law describes the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. It states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume, meaning that as the volume of a gas increases, its pressure decreases, and vice versa.
Mathematically, Boyle’s Law can be expressed as:
P₁V₁ = P₂V₂
where P₁ and V₁ represent the initial pressure and volume of the gas, and P₂ and V₂ represent the final pressure and volume.
Examples of Boyle’s Law in Action
- A balloon inflates when filled with air because the air inside the balloon exerts pressure on the balloon’s walls, which causes the balloon to expand.
- When you scuba dive, the pressure of the water around you increases as you go deeper. This increased pressure compresses the air in your lungs, reducing its volume.
Relationship between Pressure and Volume, Boyle’s and charles law gizmo answers
Boyle’s Law demonstrates the inverse relationship between pressure and volume. This means that if the pressure of a gas increases, its volume will decrease, and if the volume of a gas increases, its pressure will decrease.
This relationship is important in many applications, such as the design of scuba diving equipment and the operation of internal combustion engines.
Charles’ Law: Boyle’s And Charles Law Gizmo Answers

Charles’ Law, also known as the Law of Volumes, describes the relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas at constant pressure. It states that the volume of an ideal gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
Mathematically, Charles’ Law can be expressed as:
V/T = constant
where V is the volume of the gas, T is the absolute temperature in Kelvin, and the constant represents the initial conditions of the gas.
Examples of Charles’ Law in Action
- The expansion of a balloon filled with air when it is heated.
- The decrease in the volume of a tire when it is exposed to cold temperatures.
- The use of a gas thermometer to measure temperature based on the expansion or contraction of a gas.
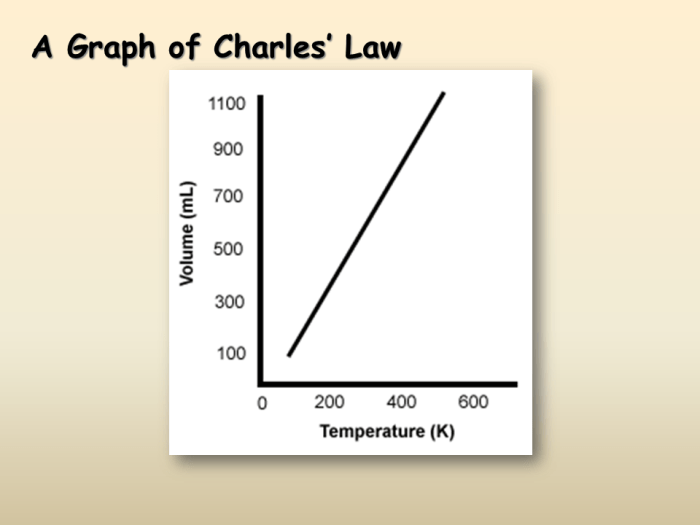
Relationship between Temperature and Volume in Charles’ Law
According to Charles’ Law, as the absolute temperature of a gas increases, its volume also increases, assuming the pressure remains constant. Conversely, as the temperature decreases, the volume of the gas decreases.
This relationship can be visualized using a graph, where the volume of the gas is plotted on the y-axis and the absolute temperature is plotted on the x-axis. The resulting graph is a straight line with a positive slope, indicating a direct proportionality between volume and temperature.
Combined Gas Law
The Combined Gas Law combines Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law into a single equation that relates pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas. It is used to solve problems involving changes in two or more of these variables.The Combined Gas Law is expressed as:“`P₁V₁/T₁ = P₂V₂/T₂“`where:* P₁ and P₂ are the initial and final pressures of the gas
- V₁ and V₂ are the initial and final volumes of the gas
- T₁ and T₂ are the initial and final temperatures of the gas
Example
A gas occupies a volume of 2.0 L at a pressure of 1.0 atm and a temperature of 273 K. What will be the volume of the gas if the pressure is increased to 2.0 atm and the temperature is decreased to 223 K?Using the Combined Gas Law:“`P₁V₁/T₁ = P₂V₂/T₂“““(1.0
atm)(2.0 L)/(273 K) = (2.0 atm)(V₂)/(223 K)“`Solving for V₂:“`V₂ = (1.0 atm)(2.0 L)(223 K)/(2.0 atm)(273 K)“““V₂ = 1.62 L“`Therefore, the volume of the gas will decrease to 1.62 L.
Applications of Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws

Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws have wide-ranging applications in everyday life, industry, and scientific research. These laws provide the foundation for understanding and predicting the behavior of gases under varying conditions.
Everyday Life
In everyday life, Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws find practical applications in various scenarios. For instance, when using a bicycle pump, Boyle’s Law explains the increase in pressure as the volume of air decreases inside the pump. This principle also governs the operation of scuba diving equipment, where the changing pressure with depth affects the volume of gas in the diver’s lungs.
Charles’ Law explains the expansion of gases with increasing temperature. This phenomenon is evident in the rising of a hot air balloon as the heated air inside expands, causing the balloon to ascend. Additionally, the law applies to the functioning of thermometers, where the expansion of a liquid or gas with temperature change is used to measure temperature.
Industry
In industry, Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws are crucial in numerous processes and applications. For example, in the production of carbonated beverages, Boyle’s Law governs the pressurization of carbon dioxide gas into the beverage. By controlling the pressure, the desired level of carbonation can be achieved.
Charles’ Law plays a significant role in cryogenic applications, such as the storage and transportation of liquefied natural gas (LNG). Understanding the expansion of gases with temperature is essential for designing and operating cryogenic storage facilities.
Scientific Research
Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws serve as fundamental principles in scientific research. In atmospheric science, these laws are used to study the behavior of gases in the atmosphere, including changes in pressure, volume, and temperature at different altitudes.
In chemistry, Boyle’s Law is applied in the study of gas kinetics and reaction rates. By manipulating pressure and volume, scientists can investigate the relationship between the concentration of reactants and the rate of a chemical reaction.
FAQ Compilation
What is Boyle’s Law?
Boyle’s Law describes the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. As pressure increases, volume decreases, and vice versa.
How is Charles’ Law different from Boyle’s Law?
Charles’ Law focuses on the direct relationship between the temperature and volume of a gas at constant pressure. As temperature increases, volume increases, and vice versa.
What is the Combined Gas Law?
The Combined Gas Law combines Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law to describe the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas under changing conditions.